Overview
|
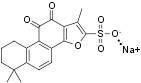
Tanshinone II-A sodium sulfonate (#T-165) is a highly pure, synthetic, and biologically active compound.
Applications
 Alomone Labs Tanshinone II-A sodium sulfonate enhances KCa1.1 channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes.A. Time course of KCa1.1 channel activity at 40 mV demonstrating the effect of 100 μM Tanshinone II-A sodium sulfonate (#T-165). B. Representative current traces under control conditions and following application of 100 μM Tanshinone II-A sodium sulfonate. Currents were elicited by a 100 ms voltage ramp from -100 to 60 mV every 10 seconds from a holding potential of -100 mV (current responses are shown between 0 and 60 mV).
Alomone Labs Tanshinone II-A sodium sulfonate enhances KCa1.1 channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes.A. Time course of KCa1.1 channel activity at 40 mV demonstrating the effect of 100 μM Tanshinone II-A sodium sulfonate (#T-165). B. Representative current traces under control conditions and following application of 100 μM Tanshinone II-A sodium sulfonate. Currents were elicited by a 100 ms voltage ramp from -100 to 60 mV every 10 seconds from a holding potential of -100 mV (current responses are shown between 0 and 60 mV).
Specifications
Technical specifications
Biological activity
- Tan, X.Q. et al. (2014) Acta. Pharmacol. Sin. 35, 1359.
Solubility and storage
Scientific Background
KCa1.1 channel is a large conductance Calcium-activated potassium channel (BKCa) known to regulate the repolarization of action potential discharge through molecular association with high voltage activated calcium channels.
Tanshinone II-A sodium sulfonate (TIIAS) is a water soluble derivative of Tanshinone IIA. Tanshinone IIA is an active constituent of the herb Danshen (Salvia miltiorrhiza) widely used in Chinese traditional medicine for coronary artery disease, hypertension and other cardiovascular diseases due to its properties of arterial dilatation. TIIAS is a synthetic opener of KCa1.1 channels with an effective concentration 10-200 μM. TIIAS increases the total permeability of BKCa in a concentration dependent manner. TIIAS has an EC50 of 111.5 μM at 0.01 μM Ca2+ and an EC50 of 68.5 μM at 0.1 μM Ca2+ 2. Similar to Danshen, TIIAS has beneficial effects on cardiac vasodilatation, reduction of oxidative stress and lipid profile. Interestingly, when used in a rat model of preeclampsia TIIAS reduced oxidative stress, however it did not lead to an improvement in pregnancy outcome criteria such as maternal blood pressure and fetal biometrics3. TIIAS was also found to have analgesic properties in neuropathic pain via inhibition of the spinal astrocytic JNK/MCP-1 pathway and the reduction of IL-1β and TNF-α expression4.
- Rehak, R. et al. (2013) Plos One 8, e61844.
- Tan, X. et al. (2011) Eur. J. Pharmacol. 656, 27.
- Morton, J.S. et al. (2015) Am. J. Physiol. 308, R163.
- Tang, J. et al. (2015) J. Neuroinflammation. 12, 57.